Hochleistungsrechnen
Hochleistungsrechen (englisch: high-performance computing, HPC) ist eine Technologie, die Rechenarbeiten ermöglicht, die einen hohen Bedarf an Rechenleistung oder Speicherkapazität haben. Somit können umfangreiche Modelle, Algorithmen oder auch Simulationen in deutlich kürzerer Zeit ausgeführt werden als es auf herkömmlichen Computersystemen möglich ist. Das Land BW stellt unter Beteiligung mehrerer Universitäten und Hochschulen – darunter auch der HFT Stuttgart – eine Hochleistungsrechenplattform bereit: BW HPC Cluster.
Beispielprojekte der HFT Stuttgart auf der Hochleistungsrechnenplatform
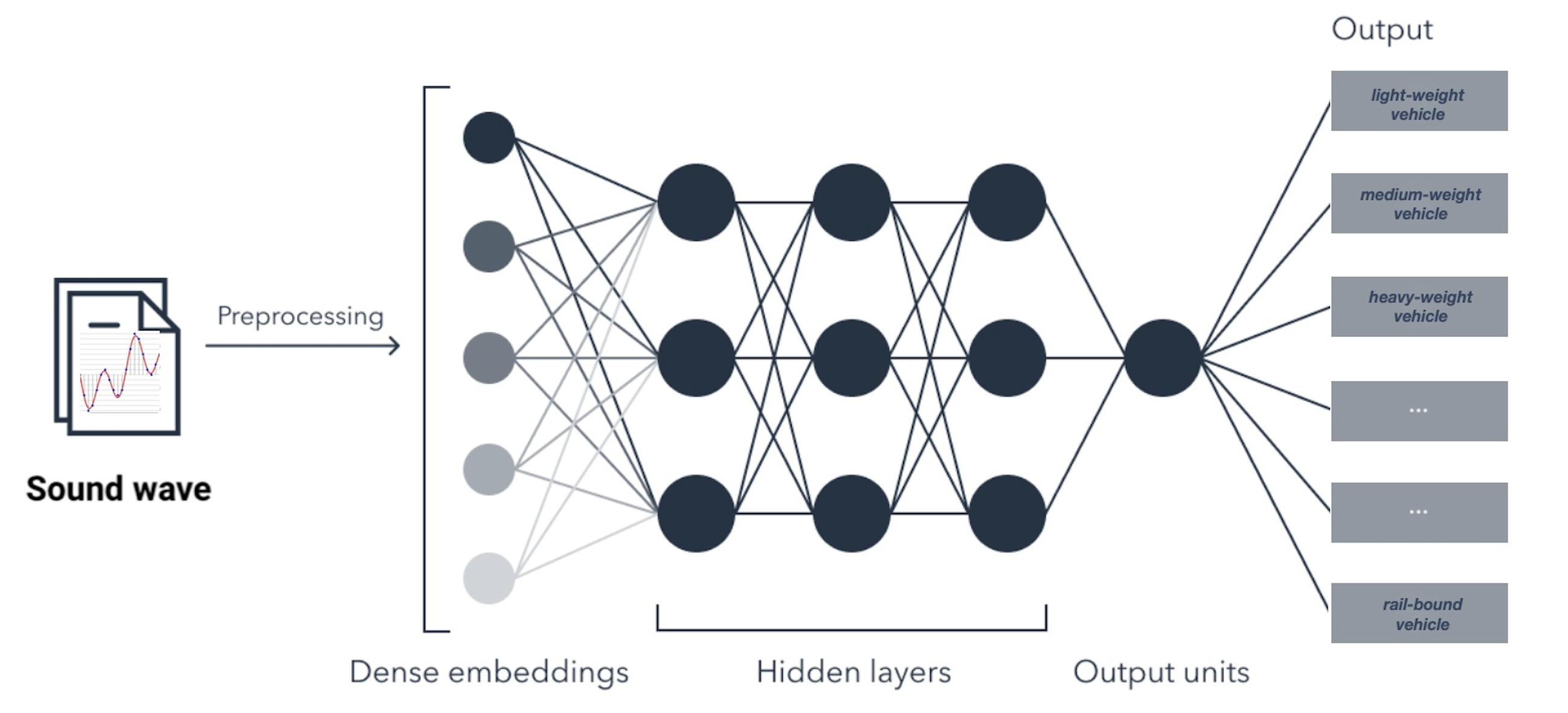
Machine Learning can work very well with image recognition, But it can also be used to recognize audio patterns. Machine Listening can be used to identify audio patterns of different entities like car engine, human speaking, nature sounds etc. Aim of this thesis is to classify different vehicles based on their sounds and then further categorize them as either light weight, medium weight, heavy weight, rail- bound or two-wheeled vehicle using the applications of Machine Listening in the field of acoustics. In order to increase the speed and performance of the software program and algorithm, the program will run on a High Performance Computing (HPC) system containing cluster which in turn will have many compute servers also called as nodes which will unable faster and parallel computing.
for more information.
In an energy community, the prosumers' interactions are critical to ensure efficient resource distribution, e.g., renewable energy sources, and to reach ambitious climate and economic goals. A typical paradigm of a local energy sharing platform consists of many prosumers and an agent that coordinates the energy transactions between prosumers. The coordinating agent, typically known as the market agent, acts according to a set of rules that enable it to match one prosumer's renewable energy surplus with the deficit of another. This article describes an agent-based modeling strategy and a case-study to demonstrate the prosumer interactions in an energy community. Each prosumer agent in the modeled environment intends to maximize its renewable energy self-consumption. At the same time, the energy community, as a whole, also would like to maximize its collective renewable self-consumption. The prosumers attempt to achieve their individual and collective objectives by following either a locally optimal or rule-based strategy. In both scenarios, prosumers have no visibility of other prosumers; therefore, the market agent has the sole responsibility of orchestrating the energy exchanges between prosumers. Finally, we discuss the significance and future research outlook for energy interaction modeling at a community scale.
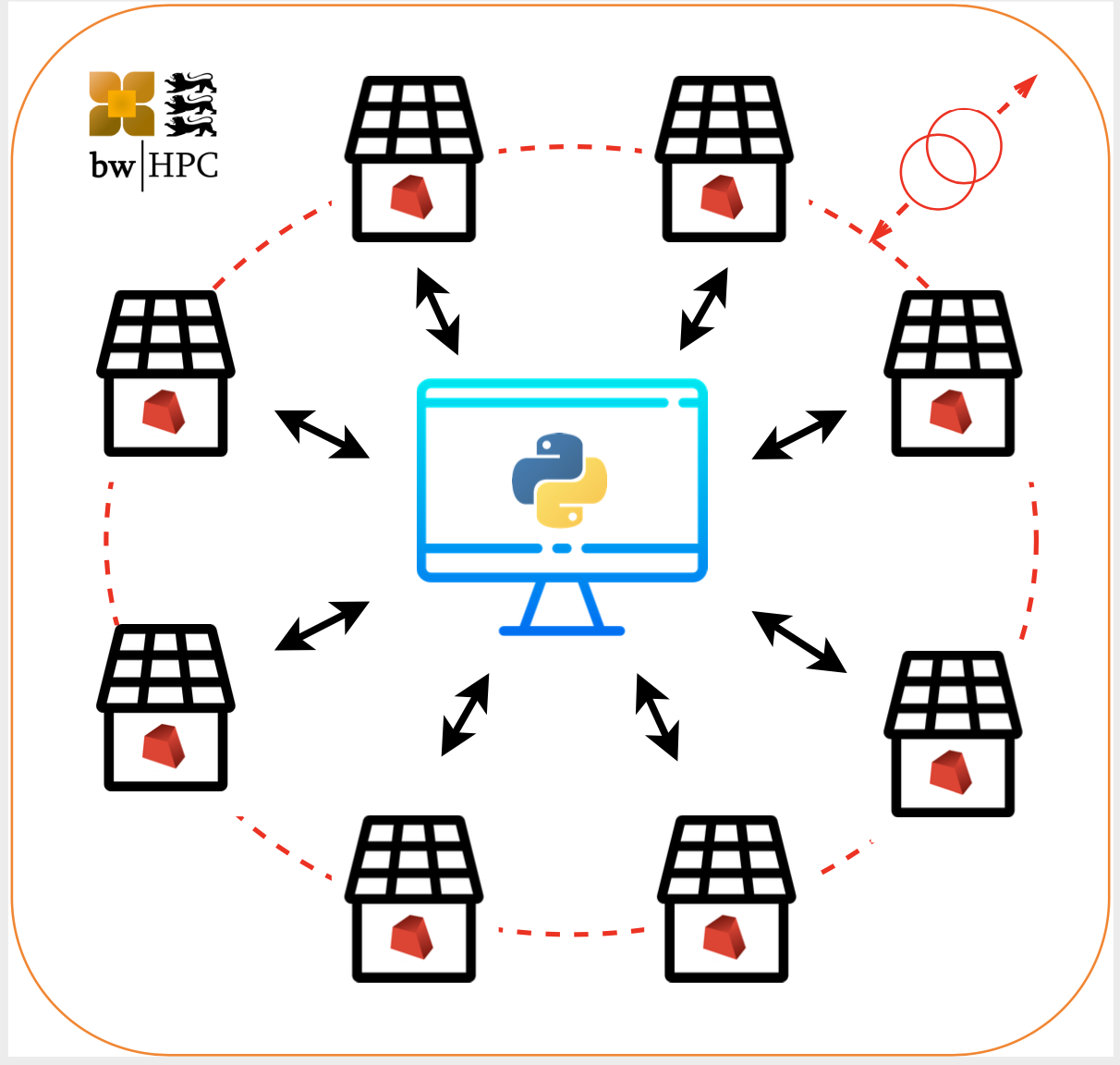
Electromobility has profound economic and ecological impacts on human society. Much of the mobility sector's transformation is catalyzed by digitalization, enabling many stakeholders, such as vehicle users and infrastructure owners, to interact with each other in real-time. This article presents a new concept based on deep reinforcement learning to optimize agent interactions and decision making in a smart-mobility eco-system. The algorithm performs context-aware, constrained-optimization that fulfills on-demand requests from each agent. The algorithm can learn from the surrounding environment until the agent interactions reach an optimal equilibrium point in a given context. The methodology implements an automatic template-based approach via a CI/CD framework using a GitLab runner and transfers highly computationally intensive tasks over a high performance compute cluster automatically without manual intervention.
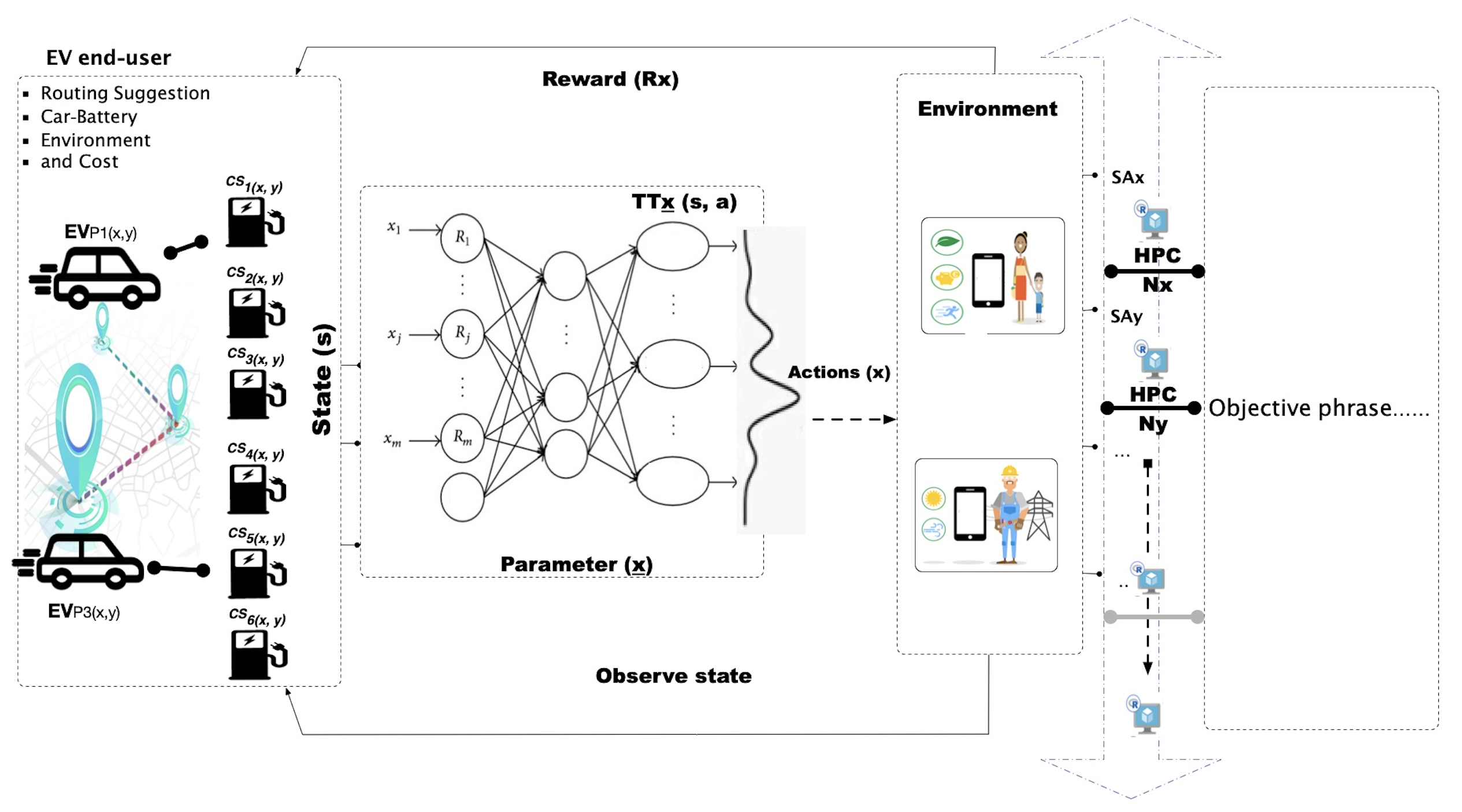
1. CA-Smart2Charge:Context-Aware optimal charging distribution using Deep Reinforcement Learning, BDIOT2020, the fourth international conference on Big Data, Singapore.
2.ARaaS:context aware optimal charging distribution as a service using deep reinforcement learning iCity_2021: Towards liveable, intelligent and sustainable future cities.